Research Achievements
Fishery Resources of Indian Himalayan region
- Fish diversity of different Himalayan rivers; Alaknanda, and Western Ramganga in Uttarakhand, Sutlej, Beas, Ravi and Chenab in Himachal Pradesh, Kameng, Siang, Tenga, Kille, Sangti, and Choskorong Kho in Arunachal Pradesh were investigated.
- Quantitative assessment of fish biodiversity and species assemblages of Himalayan rivers for the habitat/health assessment of the river based on environmental indices was studied.
- Habitat ecology and diversity of important lakes in Central and Northeastern Himalayan region was studied and a new species of copepod (Arctodiaptomus shaikhomensis) was identified from Lake Maheshwarkhand of Central Himalaya.
- Digitized maps of aquatic resources, drainage network, land use land cover, and potential fisheries development suitability maps of three districts of Arunachal Pradesh (Tawang, West Kameng and Lower Subansiri), and Leh-Laddakh region of Jammu & Kashmir using GIS tools.
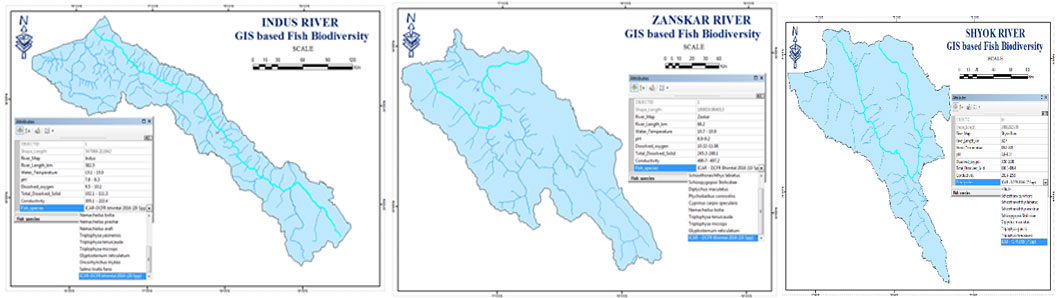
- Prepared GIS maps for habitat/distribution of ichthyofaunal resources from major drainages: Indus, Shyok, Zanskar and Jhelum of Jammu & Kashmir, Sutlej, Beas, Ravi and Chenab in Himachal Pradesh, Alaknanda, Mandakini, Pinder, Bhagirathi and Western Ramganga in Uttarakhand.
- Surveyed and explored high altitudinal lakes of the northeastern Himalayan region for the utilization of available resources. The high altitudinal freshwater lakes Sela and PTso have been explored for habitat and fish diversity in Tawang district of Arunachal Pradesh.
- The country has significant coldwater aquatic resources in terms of upland rivers, streams, high and low altitudinal natural lakes, reservoirs that hold large population of indigenous and exotic, cultivable and non-cultivable fish species. Information on resources is obsolete and updating information is a challenge due to its kaleidoscopic topography of the sector. The fishery resources of Indian Himalayan region have been digitized.
Suitable sites for aquaculture can be located based on water quality, soil quality and infrastructure facilities as road connectivity, availability of seed and etc. The weightage of the criteria were analyzed through Analytical Hierarchical Process (AHP). Resource inventory is one of the significant applications of geoinformatics in fisheries management for need based planning
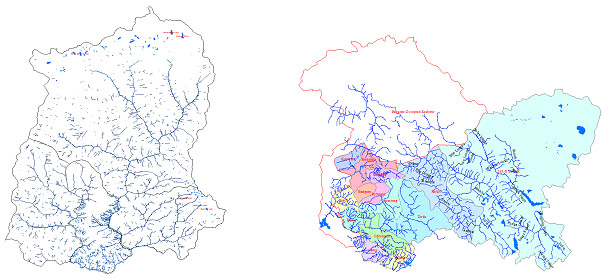
Fishery resource Map of Sikkim and Jammu & Kashmir
Primary and secondary source data on fish biodiversity were used to prepare diversity maps for different drainage in the western Himalayan region. The diversity data were joined with the physical maps of the drainages. Some important biodiversity maps are being presented hereunder:
- Eco-biological study of selected high mountain lakes in central and north-east Himalayan regions have been initiated to understand the changing trophic dynamics of the targeted lacustrine ecosystem. The hydro-biological information generated from some of the high altitudinal lakes of Arunachal Pradesh and Sikkim are the first scientific reports.
- Eco-biological study of selected high mountain lakes in central and north-east Himalayan regions have been initiated to understand the changing trophic dynamics of the targeted lacustrine ecosystem. The hydro-biological information generated from some of the high altitudinal lakes of Arunachal Pradesh and Sikkim are the first scientific reports.
- In order to develop a spatial database of coldwater resources in the Western Himalayan region, the natural water resources (rivers, lakes and reservoirs) of Jammu & Kashmir and Himachal Pradesh have been documented and digitized using satellite information and field surveys.

Fish specimens collected from Western
- Under the eco-biological study of selected Himalayan mountain lakes, a new species of copepod of the genus Hesperodiaptomus, having high concentration of carotenoids was discovered from lake Maheshwar kund situated in Munshiyari, Uttarakhand
- GIS based aquaculture site suitability maps have been generated for Kullu and Kinnaur districts of Himachal Pradesh, and Leh and Kargil districts of Jammu & Kashmir, based on physicochemical parameters of water, infrastructure facilities and input availability.
- Similarly, GIS based fish biodiversity maps for major river drainages such as Indus, Sutlej, Zanskar, Beas, Chenab and Shyok in the western Himalayan region were prepared using primary and secondary data on icthyofaunal diversity.
- Habitat ecology, population status and inter-specific variance of Schizothorax spp. in selected snow fed tributaries of Kameng drainage in Arunachal Pradesh are being studied. Preliminary analysis suggests habitat suitability for the abundance of snow trout.
- Diversity, altitudinal distribution and migration routes of endemic fishes in selected Himalayan drainages are being investigated, documented and digitized under the National Mission for Sustaining the Himalayan Ecosystem. Further, pilot carp and trout farming trials are being carried out in the identified hotspots of climate change.
- Under the national network project, coldwater fish germplasm repository centres have been established at Bhimtal and Champawat, with nearly 3400 specimens of indigenous coldwater fishes collected from different upper reach tributaries of river Ganga. For stock enhancement and conservation, breeding of Garra gotyla was successfully attempted.
- The buoyancy changing capacity of Microcystis aeruginosa which apparently allows them to migrate to different depths and its notable abundance in winter was observed in Naukuchiyatal lake ecosystem.
- Multi-tier model for integrated fish farming using polytanks in cluster approach was popularized in mid hill regions of hill states. The new model has significant improvement in fish productivity per unit area in mid hills.
- Composite carp culture including L. dyocheilus and exotic carps (silver carp, grass carp and improved Hungarian common carp) having different species composition was standardized for mid altitudes in polytanks with the higher production potential.
- Developed low cost trout raceways for the expansion of rainbow trout farming in high altitude regions Leh & Laddakh (J&K) and Uttarkashi district of Uttarakhand.
- Developed low cost recirculatory aquaculture system (RAS) for rainbow trout seed rearing.
- A prototype of zero water exchange system for egg incubation and fry rearing of coldwater fish was developed which is useful for optimal use of water and minimizing mortality during fish seed production and rearing.
- Under species diversification in coldwater aquaculture, breeding protocols were developed for Schizothorax plagiostomus, Garra gotyla, Raimas bola, Naziritor chelynoides, Nemacheilus denisoni.
- Captive rearing, breeding biology and seed production performance of Bangana devdevi, Labeo pangusia and Osteobrama belangeri, three endemic fishes of North Eastern Himalaya were evaluated.
- Multiple breeding of Neolissochilus hexagonolepis, Naziritor chelynoides, Barilius bendelisis in aquarium within a span of one year without using any synthetic or pituitary hormone or striping method have been achieved.
- Breeding of popular and indigenous ornamental fish species Garra gotyla, Garra annandalei, and Schistura obliquofascia was done for developing small scale enterprise for youth and women in hills.
- Initial success in captive breeding of golden mahseer Tor putitora for seed production has been achieved through temperature and photoperiod manipulation.
- Initial success in production of triploid rainbow trout was achieved for higher survival and faster growth which can be utilized for enhanced production in raceways culture.
- The constraints and potential of snow trout Schizothorax richardsonii as a candidate species for aquaculture was evaluated based on different intrinsic and extrinsic factors.
- Studies were taken up for developing climate resilient rainbow trout farming strategies to mitigate climate stressor under NICRA project.
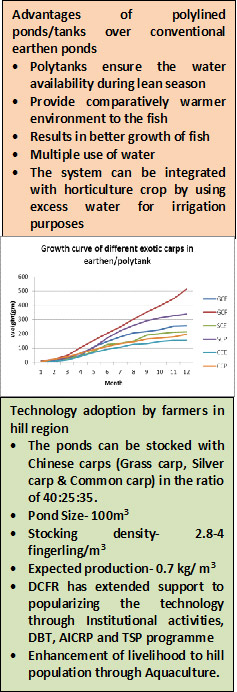
Polyculture of exotic carp in polylined tanks at mid-altitudinal regions (800-2000m MSL)
Earthen ponds lined with polythene sheets (LDPE) have been found suitable for fish culture in mid-altitudinal hill areas. These tanks are also used for rainwater harvesting in uplands areas where scarcity of water becomes major bottleneck in agricultural production. The use of polylined pond/tanks are advantageous for increasing fish production as water temperature during winter remains comparatively higher and support sustenance of natural food for growing fish.
 |  |
Induced breeding and seed production of Indigenous minor carp Labeo dyocheilus Labeo dero and Labeo pungusia
Labeo dyocheilus (McClelland) and Labeo dero (Hamilton, 1822) are important indigenous cold water fish species, endemic to the Himalayas and inhabiting upland streams and rivers at an elevation of 400-800M. Breeding and seed production technology for both the species has been developed by DCFR, Bhimtal. Water temperature ranging 18-220C found suitable for the spawning and egg incubation in coldwater condition. Successful breeding technique in captive condition enabled seed production for wild stock augmentation and species diversification in coldwater aquaculture.
First Report: Successful breeding of Chagunius chagunio and Barilius bendelisis
Chagunius chagunio, belongs to family cyprinidae commonly known as “Chaguni” is one of the economically important indigenous fish having its distribution in Brahmaputra and Ganga drainages along the Himalayan foot hills. In Kumaon Himalayan region, C. chagunio is locally called as “Chippan” has high consumer preference and fetch very good market price of about Rs. 300/kg. Captive reared brood stock of this minor carp was successfully bred under coldwater conditions and breeding protocol was developed for the seed production.
The hill trout cyprinid, Barilius bendelisis (Hamilton), has recently drawn the attention as one of the potential candidate species for aquaculture. It is commonly distributed in Brahmaputra and Ganga drainages along the Himalayan foot hills. As per IUCN red list (2012) this fish has been categorized as least concern but in future the major threat to this species is over exploitation, habitat destruction due to natural and human interruption. Therefore, in order to overcome this problem, breeding and propagation of B. bendelisis is a prerequisite task to replace the stock. Barilius bendelisis being a demanding ornamental as well as potential food fish has not received any research attention for breeding and seed production and fish has been successfully bred for first time.
Captive breeding of Labeo pungusia
Labeo pungusia is threatened species as per IUCN but having good potential for food fish in North-Eastern India. To conserve and rehabilitate the species, successful breeding achieved at Eco-camp, ABACA, Nameri, Assam for conservation and species diversification of aquaculture in North East hill region.
Pond culture of Bangana devdevi
Bangana devdevi is potential species of Manipur, locally known as Khabak. Hence, ICAR-DCFR with Krishi Vigyan Kendra, Thoubal, Manipur have undertaken initiative to culture this fish in farmers pond.
- Rearing of fingerlings of Himalayan Golden Mahseer (Tor putitora) in floating cages
Open water bodies in hills provides opportunities for in situ seed rearing in floating cages which may be used for the stock enhancement programmes. Protocol for in situ rearing density of golden mahseer upto advanced fingerling stage have been developed with appropriate stocking density and feeding practices.

- Photothermal induced changes in the profile of reproductive hormones has been recorded and aromatase encoding genes were partially characterized. Full length cDNA of kisspeptin1, kisspeptin1 receptor and kisspeptin2 of golden mahseer were cloned and characterized. Further, the structural analysis of the predicted kiss1 and kiss1r peptides have been carried out to support in vivo physiological studies.
- A broad ranging project has been taken up to decipher the physiological mechanisms underlying nutrient mediated regulation of growth and maturation in Schizothorax richardsonii. Wild collected snow trout have been successfully acclimatized and reared in captivity. The effect of nutritional status on growth physiology is being experimentally elucidated. Concurrently, captive breeding of farm raised brooders have been achieved. The biochemical composition, fatty acid profile, cholesterol, triglyceride and mineral concentration of six different snow trout species has been estimated to accentuate its nutritional value as a dietary component for human consumption.
- For the first time, observation of reproductive behaviour, captive breeding, larval rearing and seed production of Neolissochilus hexagonolepis, Barilius bendelisis and Naziritor chelynoides has been achieved in controlled glass aquaria conditions.
- A prototype zero water exchange glass aquarium hatchery with sand-gravel bed filtration system was successfully developed and used for egg incubation and larval rearing of minor carp (Labeo dyocheilus) and rainbow trout.
- The feasibility of composite carp farming at high altitudes in polyhouse covered polylined ponds/tanks is being assessed through field experimentation. Preliminary observation indicated better growth of grass carp and improved common carp in this culture system.
- Effect of temperature on the gonadal maturation of golden mahseer was experimentally elucidated in captivity. Higher rearing temperature resulted in elevated concentrations of estradiol and progesterone in females, however with concurrent decrease in the plasma levels of cortisol and total immunoglobulins. Further, for molecular assessment of captive maturation in golden mahseer, the complete coding sequence of two isoforms of aromatase brain type (cyp19b) has been characterized.
- The gene expression profile of kisspeptin1 and its receptor in the brain-pituitary-gonad axis of wild collected adult male and female golden mahseer during different gonadal developmental stages has been explicated.
- Seed production of important coldwater fishes such as improved Hungarian common carp (7.29 lakh fry), golden mahseer (65,000 fry), rainbow trout (56,000 fry), snow trout (38,000 fry) and ornamental fishes was carried out. The revenue generated from the sale of carp, mahseer and ornamental fish seed amounted to 2.74 lakh rupees.
Promotion of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) farming in Sikkim
The Directorate has provided technical support to state for promotion of trout culture. State has achieved total production of rainbow trout around 110 tonnes from both public sector and in private sector having 220 private trout raceways in the state. Most of the production is consumed locally in households and in some high class hotels. Trout farming is a viable livelihood option for the local population with high market demand in the higher altitudinal areas. A constant technical support has been provided by the DCFR, Bhimtal for infrastructural development, brood stock maintenance and seed production, feed formulation including advisory service and hands on training to the trout growers. Healthy brood stock of Rainbow trout has been maintained at State trout farm, Uttarey and produced 1.5 lakh advanced fingerlings and 3 lakh eyed ova of Rainbow trout during this breeding season. A wooden stripping stand was designed by DCFR for easy stripping operation and to reduce the man power, physical stress on brooder and on breeder during stripping operation. The device was practically demonstrated to the farmers.
DCFR rehabilitated natural disaster affected 6 tribal farmer’s families at Upper Rimbi, West Sikkim and provided financial & technical support for raceway renovation, trout seed stocking and trout feed. Seed of Rainbow trout was stocked in those renovated raceways during the month of May, 2014 and achieved good growth with best management practices. Technical advice was provided to the trout growers for maintaining sufficient water flow, appropriate design of outlet, optimum stocking density and feeding management. Individual selection of the brood stock was carried at Uttarey for the stock improvement with the target of 5 lakh eyed ova production in the next breeding season
Promotion of trout culture in Highlands of Leh & Ladakh

Leh- a tribal district has low opportunity of agriculture due to harsh climatic conditions while trout culture can be adopted as small scale enterprises which can provide round the year livelihood support to the dwellers. ICAR-Directorate of Coldwater Fisheries Research, Bhimtal has initiated trout faming programme under Tribal Sub Plan for improving socio-economic status of the tribal population during 2013-14 in collaboration with HMAARI (SKUAST-K) RRS- CAZRI (ICAR)-Leh and Department of Fisheries, Govt. of Jammu & Kashmir. Initially three (3) existed raceways were repaired and 5 new raceways were got constructed in Chushout Shamma village which is about 20 km from the Leh and located near the bank of a tributary of River Indus at 3280 meter above sea level. Presently, six (6) tribal families are covered under trout farming programme and a total of 13 trout raceways have been created. Technical know-how and inputs (trout seed and feed) provided to the farmers.
- Successful larval rearing of Barilius bendelisis, Puntius ticto, Naziritor chelynoides, N. hexagonolepis in controlled condition in Aquarium was achieved with zero water exchange system.
- A broad ranging project has been taken up to decipher the physiological mechanisms underlying nutrient mediated regulation of growth and maturation in Schizothorax richardsonii. Wild collected snow trout have been successfully acclimatized and reared in captivity. The effect of nutritional status on growth physiology is being experimentally elucidated. Concurrently, captive breeding of farm raised brooders have been achieved.
- Two efficient and cost-effective single and multiple protein based starter feeds were formulated for initial feeding of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) fry providing higher survival and better FCR values.
- Formulated a standard vitamin-mineral premix for rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) based on the known nutritional requirements. This premix was found to be an effective feed supplement.
- Formulated a brooder feed for golden mahseer with maturation enhancing nutrients such as tryptophan, phospholipids, folate, ascorbate and tocopherol. Feeding this formulation along with photo-thermal manipulations aided captive maturation and spawning.
- Appetite markers were developed to standardize feeding strategy for faster growth of golden mahseer juveniles.
- Digestive ontogeny of golden and chocolate mahseer has been elucidated based on histomorphological and enzymatic changes. This understanding will help in minimizing the mortalities during endogenous to exogenous feed transition and larval rearing.
- An azolla based farm made wet feed having optimum protein requirement for carp was formulated and popularized in mid hill regions.
- Nutrient uptake and feed ingestion in snow trout (Schizothorax richardsonii) was studied in relation to gut microbial composition due to wild-captivity transition, diet composition, rearing temperature and prophylactic treatments.
- The protein and lipid requirement of snow trout (Schizothorax richardsonii) was tested and potential optimum inclusion levels were identified based on growth response.
- Thirty two molecular biomarkers for feed use, metabolism and growth have been characterized in snow trout (Schizothorax richardsonii). This includes genes encoding digestive enzymes, GH-IGF axis component proteins, myogenic regulatory factors, metabolic enzymes and feed intake regulatory peptides.
- In the context of fish meal replacement and sustainability, the efficacy of two alternate protein sources (industrial by-products), namely rice derived high protein distiller’s dried grains and methanotrophic bacterial meal have been comprehensively evaluated and their optimum inclusion levels in rainbow trout grow-out feed has been ascertained.
- Nutrient quality of important coldwater food fishes of entire (western to eastern) Himalaya, and small indigenous fish species (SIFs) from Brahmaputra river and its tributaries were evaluated and their nutrient contribution potential was also calculated for dietary recommendation.
- Protocols for the successful culture of Chlorella and rotifer for feeding of mahseer larvae were developed
- The protocol for preparation of microparticulate diet for golden mahseer larvae has been established and based on this protocol, a microparticulate diet “NANHE MAHSEER” for feeding of golden mahseer, Tor putitora larvae has been developed and evaluated.
- Cost effective growout feed with 1.43 FCR has been developed and evaluated for culture of chocolate mahseer, Neolissocheilus hexagonolepis.
- Cost effective and efficient starter and growout feed with an FCR of 1.26 has been developed and field tested for rearing of rainbow trout
- Formulated larval feed for snow trout is useful to rear the fry with 62% survival. Seed production in controlled condition and its ranching in rivers & streams is the priority of hill states and Hydro Electric projects to augmentation of wild population of this important indigenous species.
- Grow out feed for the snow trout has formulated with minimum use of fish meal.
- Starter rainbow trout feed is prepared with blend of animal & plant protein, which is more efficient over the commercial feed and is a cost effective feed.
- Grow out feed for rainbow trout has formulated with minimum use of fish meal & fish oil.
- Farm made trout feed using fish offal/poultry offal has been demonstrated to the farmers of Sikkim & Himachal Pradesh. This readily available material based feed is using by the farmers as emergency feed, when commercial feed is not readily available for a short period.
- Two cost-effective practical starter feeds were formulated for first feeding rainbow trout fry, based on single or multiple protein sources. The experimental diets were made up of commercial ingredients and were conventionally prepared by steam cooking, pelleting and drying. To evaluate the performance of these two diets as compared to a widely used commercial diet, a five week feeding trial was conducted and found more efficient over the commercially used starter feed.
- Goblet cell dynamicity in digestive tract, zymogen granule dynamicity in pancreas and supra-nuclear vesicles in hindgut were microscopically ascertained to be histological markers of appetite in early life stages of golden mahseer.
- The lipid metabolism of snow trout (Schizothorax richardsonii) was found to dynamically respond to feed availability and deprivation, in terms of whole body lipid content, plasma triglycerides, viscerosomatic index and volume of hepatocytes.
- Based on growth response to graded levels of dietary protein, the optimum dietary protein requirement of snow trout was found to be apparently high (45-50%). However, poor feed utilization (FCR of 7-15) could be a major reason for the slow growth of this species.
- A robust and inexpensive RACE methodology has been developed for full length characterization of cDNA, and 26 partial or complete nucleotide sequences of markers related to digestion, metabolism, growth and maturation of snow trout were obtained.
- Comparative analysis of the intestinal bacterial composition, abundance and dynamics in captive and wild snow trout revealed a decrease in bacterial diversity with the transition from wild to captivity. Cetobacterium somerae was the most abundant species.
- Comparative analysis of extruded and pelleted rainbow trout starter feed indicated that the method of feed preparation and pellet integrity has a direct relevance to hatchery management, in terms of survival and water quality.
- Based on the estimated nutritional quality of selected endemic fish species, Setipinna phasa, Semiplotus semiplotus and Barilius bendelisis showed more than 100% potential contribution of fatty acids and minerals to recommended daily allowance.
- The complete mitochondrial genome for three major coldwater fishes: Neolissochilus hexagonolepis (Chocolate mahseer), Salmo trutta fario (brown trout) and Cyprinion semiplotus (Assamese kingfish) was determined for the first time. This study will provide the rationale for the management and conservation of the endemic coldwater fish species.
- Mitochondrial makers for three important coldwater fish species were developed and genetic diversity of different populations was estimated. The study provides stock-specific strategies for breeding and conservation of the wild population of coldwater species.
- A total of 37 novel microsatellite markers in important coldwater fish species; Neolissochilus hexagonolepis (Chocolate mahseer) and Salmo trutta fario (brown trout) were developed and population structure was determined. The microsatellite markers developed can be used for future population genetics studies and long-term endeavors such as genome mapping, localization of quantitative trait loci and the implementation of marker-assisted selection.
- Genetic stock assessment of farmed brown trout (Salmo trutta fario) was done to assess the genetic diversity of the available stocks in India and their inbreeding status.
- Peptide synthesis facility has been established and protocol for chemical synthesis of peptides using Fmoc-chemistry in the laboratory has been optimized.
- A comprehensive transcriptome dataset for T. putitora has been generated by sequencing the gonads and brain of both sexes using the Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) platform. The transcriptome dataset developed will lead to develop sex specific marker for early identification of sex in mahseer.
- Multiplex PCR for the rapid detection of E. coli in food samples was standardized.
- De Novo whole genome sequencing of Fictibacillus phosphorivorans, having algicidal properties was done using NGS technology.
- Procedure for the culture of fish cells from different organs of snow trout (Schizothorax richardsonii) has been standardized.
- Five myogenic regulatory transcripts (myod, myog, myf5, myf6 and mstn1) were characterized to understand the slow growth mechanism in Schizothorax richardsonii (snow trout).
- Adaptive mechanisms in coldwater fishes for tolerance of adverse conditions lead to changes in the physiological and metabolic activities of the fishes. Studies were conducted to understand the skewed sex ratio and gender specific response to thermal stress in golden mahseer in Himalayan region.
Genomic Resources
1. Mitochondrial DNA sequences:
Table: Mitochondrial DNA sequences
| Species | Cyt b | ATPase6/8 | COI | COII | 16 SrRNA |
| Tor putitora | 170 | 161 | 6 | 10 | |
| Tor khudree | 4 | ||||
| Tor chelynoides | 4 | ||||
| Neolissochilus hexagonolepis | 5 | ||||
| Schizothorax richardsonii | 47 | 25 | 22 | 25 | 10 |
| Schizothorax progastus | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | |
| Schizopyge niger | 3 | 5 | 5 | 5 | |
| Schizothorax esocinus | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | |
| Barilius bendelisis | 15 | 6 | |||
| Garra gotyla | 8 | ||||
| Acanthocobitis botia | 2 | ||||
| Schistura obliquofascia | 5 | ||||
| Schistura rupecula | 7 | ||||
| Glossogobius gutum | 6 | ||||
| Glossogobius giuris | 4 | ||||
| Glossogobius spp. | 6 |
2. Complete Mitochondrial Genome Organization of Coldwater Fish Species
The complete mitochondrial genome of important coldwater fish species under genus Schizothorax (snow trout) and Tor (mahseer) was determined for the first time. This study will provide the rationale for the management and conservation of the endemic coldwater fish species.
Table: Details of complete mitochondrial genomes of different coldwater fish species
| Species | Genome Size (bp) | GenBank | Protein coding genes | tRNA | rRNA | A + T content | G + C content |
| Schizothorax richardsonii | 16,592 | KC790369 | 13 | 22 | 2 | 55.4% | 44.6% |
| S. labiatus | 16,582 | KF739398 | 13 | 22 | 2 | 55.3% | 44.7% |
| S. progastus | 16,575 | KF739399 | 13 | 22 | 2 | 55.2% | 44.8% |
| S. esocinus | 16,583 | KF600713 | 13 | 22 | 2 | 55.2% | 44.8% |
| S. plagiostomus | 16,576 | KF928796 | 13 | 22 | 2 | 55.8% | 44.2% |
| Schizopyge niger | 16,585 | NC_022866 | 13 | 22 | 2 | 55.2% | 44.8% |
| Tor putitora | 16,576 | KC914620 | 13 | 22 | 2 | 56.9% | 43.1% |
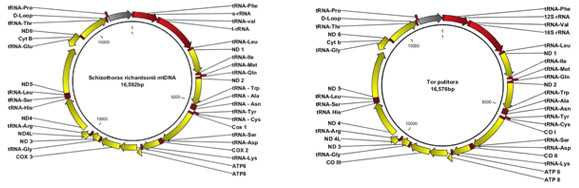 | |
| Mitochondrial Genome organization of S. richardsonii | Mitochondrial Genome organization of Tor putitora |
3. Development of Microsatellite Markers
Microsatellite markers in important coldwater fish species were developed. The informative loci can be used for population genetics studies and long-term endeavours such as genome mapping, localization of quantitative trait loci and the implementation of marker-assisted selection.
Table: Development of microsatellite marker from genomic library
| Species | No. of Markers developed | GenBank |
| Schizothorax richardsonii | 51 26 (ESTs SSR) | HM591233-HM591283 JK087- 411, 471, 486, 532, 553, 716, 738, 740, 763, 886, 902, 903, 992, JK088032, 043, 048, 052, 064, 073, 103, 106, 195, 201, 219, 319, 390 |
| Schizopyge niger | 12 | KC339275-KC339286) |
| Garra gotyla | 52 | HQ288484-HQ288526 & JF268657-JF268665 |
| Tor putitora | 22 34 (EST SSR) | JX270775-JX270794 |
| Schistura sikmaiensis | 36 | KJ545923-KJ545958 |
| Neolissocheilus hexagonolepis | 12 | validation in process |
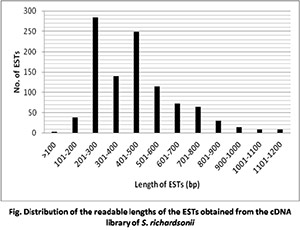
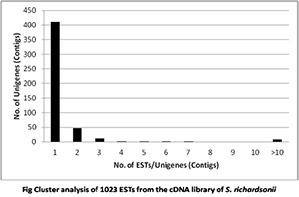
4. Development of EST Markers from cDNA of Schizothorax richardsonii
The snow trout (Schizothorax richardsonii) is an economically important fish in the north-east Himalayan region. However, genomic research on this species is still in its infancy, and genomic resources are largely unavailable. The objective of this study was to generate expressed sequence tags (ESTs) from a brain complementary DNA (cDNA) library and to identify the genes. A total of 1031 ESTs were sequenced, from which 73 contigs and 411 singletons were identified. BLAST homology analysis indicated that only 9.3% of these ESTs were homologues of known genes while the remaining 90.7% appeared to be novel sequences. Based on sequence similarities, 45 putative genes were identified that encodes stress proteins, enzymes and signal transduction regulators. Our study thus, provides a collection of novel transcripts and a partial annotation of genes that are expressed in brain tissue of the snow trout species, S. richardsonii
| Table: ESTs from cDNA of Schizothorax richardsonii | |||||||||||||||||||
|    | ||||||||||||||||||
Species and Population Characterization of Coldwater Fishes Using Mitochondrial and Microsatellite Markers
1. Novel species identification – Schistura obliquofascia, a new loach from Uttarakhand, India
- Amplicon of 307 bp of Cyt b region of the mtDNA was amplified using Universal Primers (Kocher et al. 1989).
- L14841AAAAAGCTTCCATCCAACATCTCAGCATGATGAAA
- H15149-AAACTGCAGCCC CTCAGAATGATATTTGTCCTCA
- Sequences of the mitochondrial Cyt b genes of the other two species of Schistura and Schizothorax richardsonii were used for phylogeny.
- Neighbor-joining tree and genetic distance data show S. corica to be genetically distant from the S. obliquofascia and S. beavani.
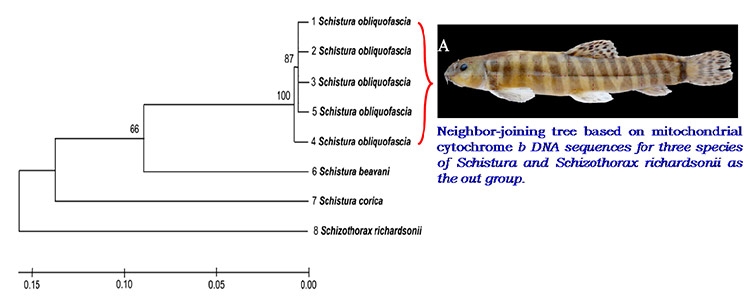
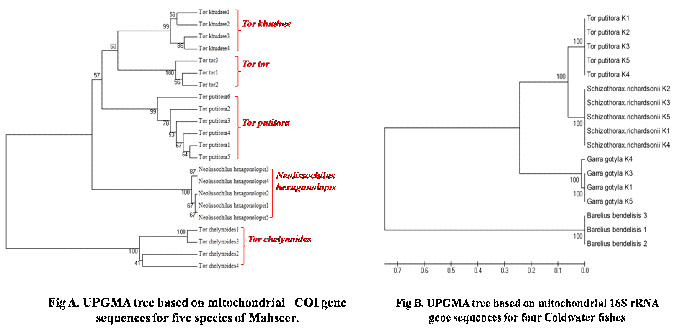
2. Species characterization using mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA)
| Species were characterized using mtDNA (Cytb, ATPase 6/8, Cytochrome Oxidase I, Cytochrome Oxidase II and 16 SrRNA) markers. |
|